Python en Ingeniería Civil
| Sitio: | Facultad de Ingeniería U.Na.M. |
| Curso: | Informática ET241/EM241/IC241/IN241/IM204 |
| Libro: | Python en Ingeniería Civil |
| Imprimido por: | Usuário visitante |
| Día: | martes, 19 de agosto de 2025, 22:17 |
Descripción
Estos ejercicios son para demostrar a los alumnos el uso de Python en la resolución problemas en el ámbito de la Ingeniería Civil
1. Cálculo de un Silo.
Este código de Python hecho por un alumno de Ing. Civil y enviado por el Ing. Javier Duarte, permite calcular datos sobre un silo.
Utiliza la librería : matplotlib
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Aug 27 22:54:33 2020
@author: Maria Belen
"""
#--------------Importar PI----------------------------
import math
PI=math.pi
#--------------Mostrar imagen-------------------------
#La imagen silos.jpg debe estar en el mismo directorio que el script de Python
from PIL import Image
im = Image.open('silos.jpg')
im.show()
print('') print('CALCULADORA DE VOLUMEN'.center(50,"=")) print('') #-------------Funcion calcular contenido------------------------
def calculo():
f=((39)**(1/2))/4
while True:
try:
t=float(input('Ingrese el espesor de los bordes del silo en metros entre [0:{:.3f}]: '.format(2-f))) if t>0 and t<2-f:
break
else:
print('Ingrese un grosor entre [0;{:.3f}]'.format(2-f)) except ValueError:
print('Ingrese un numero. Reintente') continue
#print('La altura "h" que se hace referencia es la mostrada en la figura') while True:
try:
h=float(input('Ingrese la altura "h" en metros que puede estar entre [-2,23;5,27]: ')) if h>=-2.23 and h<=5.27:
break
else:
print('Ingrese un numero valido') continue
except ValueError:
print('Reintente. Ingrese un número') continue
contenido=input('Ingrese el nombre del contenido del silo: ') while True:
try:
densidad=float(input('Ingrese la densidad del {} en kg/m3: '.format(contenido))) if densidad>0:
break
else:
print('Ingrese densidad mayor a cero') continue
except ValueError:
print('Ingrese un numero. Reintente') continue
f=((39)**(1/2))/4
if h>=(-2.23) and h<=(-1.73) :
V1=PI*((0.5-t)*(2.23+h-t)**2-((2.23+h-t)**3)/3)
masa1=V1*densidad
print('') print('Si hay una altura {} m de {}, posee un volumen de {:.3f} m3 con un masa de {:.3f} Kg'.format(h,contenido,V1,masa1)) elif h>(-1.73) and h<=(0) :
r1=0.5-t
h1=-1.73
V1=PI*((0.5-t)*(2.23+h1-t)**2-((2.23+h1-t)**3)/3)
V2=PI*((1.73+h)*r1**2+((75/173)**2)*((1.73+h)**3)/3+(75/173)*r1*(1.73+h)**2)
V12=V1+V2
masa12=V12*densidad
print('') print('Si hay una altura {} m de {}, posee un volumen de {:.3f} m3 con un masa de {:.3f} Kg'.format(h,contenido,V12,masa12)) elif h>(0) and h<=(3.27+f) :
r1=0.5-t
h1=-1.73
V1=PI*((0.5-t)*(2.23+h1-t)**2-((2.23+h1-t)**3)/3)
h2=0
V2=PI*((1.73+h2)*r1**2+((75/173)**2)*((1.73+h2)**3)/3+(75/173)*r1*(1.73+h2)**2)
V3=(5/4)**2*PI*h-PI*t*h
V123=V1+V2+V3
masa123=V123*densidad
print('') print('Si hay una altura {} m de {}, posee un volumen de {:.3f} m3 con un masa de {:.3f} Kg'.format(h,contenido,V123,masa123)) elif h>(3.27+f) and h<=(5.27):
r1=0.5-t
h1=-1.73
V1=PI*((0.5-t)*(2.23+h1-t)**2-((2.23+h1-t)**3)/3)
h2=0
V2=PI*((1.73+h2)*r1**2+((75/173)**2)*((1.73+h2)**3)/3+(75/173)*r1*(1.73+h2)**2)
h3=3.27+f
V3=(5/4)**2*PI*h3-PI*t*h3
r4=2-t
V4=(r4**2*PI*(h-3.27-f-t)-(PI/3)*(((h-3.27-t)**3)-(f)**3))
V1234=V1+V2+V3+V4
masa1234=V1234*densidad
print('') print('Si hay una altura {} m de {}, posee un volumen de {:.3f} m3 con un masa de {:.3f} Kg'.format(h,contenido,V1234,masa1234)) #-----------------Funcion Volumen total--------------
def vol_total():
f=((39)**(1/2))/4
r1=0.5
h1=-1.73
V1=PI*((0.5)*(2.23+h1)**2-((2.23+h1)**3)/3)
h2=0
V2=PI*((1.73+h2)*r1**2+((75/173)**2)*((1.73+h2)**3)/3+(75/173)*r1*(1.73+h2)**2)
h3=3.27+f
V3=(5/4)**2*PI*h3
r4=2
h4=5.27
V4=(r4**2*PI*(h4-3.27-f)-(PI/3)*(((h4-3.27)**3)-(f)**3))
V1234=V1+V2+V3+V4
return V1234
#-----------------Funcion volumen contenido---------------
def vol_contenido(t):
f=((39)**(1/2))/4
r1=0.5-t
h1=-1.73
V1=PI*((0.5-t)*(2.23+h1-t)**2-((2.23+h1-t)**3)/3)
h2=0
V2=PI*((1.73+h2)*r1**2+((75/173)**2)*((1.73+h2)**3)/3+(75/173)*r1*(1.73+h2)**2)
h3=3.27+f
V3=(5/4)**2*PI*h3-PI*t*h3
r4=2-t
h4=5.27
V4=(r4**2*PI*(h4-3.27-f-t)-(PI/3)*(((h4-3.27-t)**3)-(f)**3))
V1234_contenido=V1+V2+V3+V4
return V1234_contenido
#------------------Funcion calcular bordes----------------
def bordes1234():
f=((39)**(1/2))/4
while True:
try:
t=float(input('Ingrese el espesor de los bordes del silo en metros entre [0:{:.3f}]: '.format(2-f))) if t>0 and t<2-f:
break
else:
print('Ingrese un grosor entre [0;{:.3f}]'.format(2-f)) except ValueError:
print('Ingrese un numero. Reintente') continue
volumen_total=vol_total()
volumen_contenido=vol_contenido(t)
bordes=volumen_total-volumen_contenido
return bordes
#------------------Programa MENU----------------------------
while True:
print('') print('MENU'.center(50,"-")) print('') print('Elija que desea hacer:\n\n1-Calcular volumen y masa de contenido\n2-Volumen bordes\n3-Volumen total\n4-Salir') try:
print('') eleccion=int(input('Su eleccion: ')) if eleccion==1:
calculo()
elif eleccion==2:
bordes1=bordes1234()
while True:
try:
print('') densidad12=float(input('Ingrese la densidad de los bordes en kg/m3: ')) if densidad12>0:
break
else:
print('Ingrese densidad mayor a cero') continue
except ValueError:
print('Ingrese un numero. Reintente') continue
densidad_bordes=bordes1*densidad12
print('') print('El volumen de bordes es de: {:.4f} m3 y la masa es de {:.3f} kg'.format(bordes1,densidad_bordes)) elif eleccion==3:
print('') print("El volumen total es {:.3f} m3".format(vol_total())) elif eleccion==4:
print('') print('Finalizando programa....') break
else:
print('Ingrese opcion valida') continue
except ValueError:
print('Ingrese una opcion. Reintente') continue
1.1. Imagen de Silo
Descargar esta imagen y guardar como silos.jpg en el mismo diretorio que el script .py
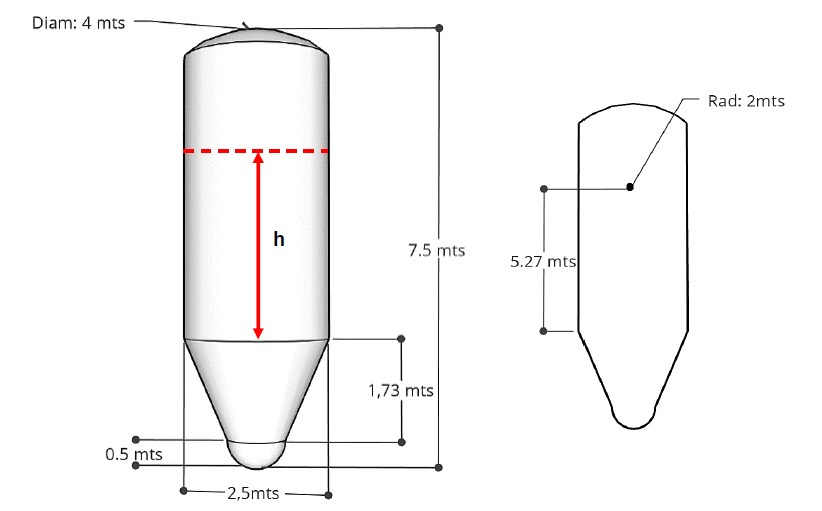
2. Cálculo de Tensiones en Tensor
Este código de Python hecho por
grupo de alumnos de Ing. Civil y enviado por el Ing. Javier Duarte, permite las tensiones sobre los tensores de una estructura.
Utiliza la librería : numpy
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Oct 13 10:13:59 2020
@author: Grupo 10
"""
#IMPORT
import numpy as np
#FUNCIONES
def Invariantes_escalar(matriz1,matriz2):
sum1=0
sum2=0
for i in range(3):
sum1+=matriz1[i,i]
sum2+=matriz2[i,i]
sum1=round(sum1)
sum2=round(sum2)
lista=[]
lista.append(sum1)
lista.append(sum2)
if sum1==sum2:
return True,lista
else:
return False,lista
def Det_menor(matriz1,matriz2):
vec1=[ ((float(matriz1[1,1])*float(matriz1[2,2])) - (float(matriz1[2,1])*float(matriz1[1,2])) ), ( (float(matriz1[0,0])*float(matriz1[2,2])) - (float(matriz1[2,0])*float(matriz1[0,2])) ),((float(matriz1[0,0])*float(matriz1[1,1])) - (float(matriz1[1,0])*float(matriz1[0,1])) )]
vec2= [((float(matriz2[1,1])*float(matriz2[2,2])) - (float(matriz2[2,1])*float(matriz2[1,2])) ), ( (float(matriz2[0,0])*float(matriz2[2,2])) - (float(matriz2[2,0])*float(matriz2[0,2])) ),((float(matriz2[0,0])*float(matriz2[1,1])) - (float(matriz2[1,0])*float(matriz2[0,1])) )]
sumvec1=0
sumvec2=0
for i in vec1:
sumvec1+=i
sumvec1=round(sumvec1)
lista=[]
lista.append(sumvec1)
for i in vec2:
sumvec2+=i
sumvec2=round(sumvec2)
lista.append(sumvec2)
if sumvec1== sumvec2:
return True,lista
else:
return False,lista
def Det_mayor(matriz1,matriz2):
m1=np.linalg.det(matriz1)
m1=m1.round()
m2=np.linalg.det(matriz2)
m2=m2.round()
lista=[]
lista.append(m1)
lista.append(m2)
if m1==m2:
return True,lista
else:
return False,lista
def carga():
lista1=[0.0,0.0,0.0]
lista2=[0.0,0.0,0.0]
lista3=[0.0,0.0,0.0]
for i in range(3):
while True:
try:
a=float(input('Inserte el valor de a1{}: '.format(i+1))) lista1[i]=a
break
except ValueError:
print('Dato erróneo. Reintente.') for j in range(3):
while True:
try:
a=float(input('Inserte el valor de a2{}: '.format(j+1))) lista2[j]=a
break
except ValueError:
print('Dato erróneo. Reintente.') for k in range(3):
while True:
try:
a=float(input('Inserte el valor de a3{}: '.format(k+1))) lista3[k]=a
break
except ValueError:
print('Dato erróneo. Reintente.') matriz=np.array([lista1,lista2,lista3])
return matriz
#PROGRAMA
print('Diagonalización de tensor de tensiones.'.center(50,'-')) M=np.array([[8,2,1],[2,6,1],[1,1,3]])
while True:
print('Menú de opciones:') print('1. Cargar tensor \n2. Calcular Tensiones y Direcciones Principales \nS. Salir ') print('(Se aclara que por defecto está cargada la matriz T de la AEP n° 2)') opcion=input('¿Qué desea hacer? ') if opcion=='1':
M=carga()
elif opcion=='2':
print('La MATRIZ propuesta es:') print(M)
valores,vectores=np.linalg.eig(M)
print('Esta matriz es un Tensor de Inercia.') print('') #AUTOVALORES
print('Los AUTOVALORES son:') for i in valores:
print(i.round(2))
print('Estos autovalores representan las Tensiones Principales.') print('') print('La matriz de autovalores queda:') N=np.array([[float(valores[0].round(2)),float(0),float(0)],[float(0),\
float(valores[1].round(2)),float(0)],[float(0),float(0),float(valores[2].round(2))]])
print(N)
print('') #AUTOVECTORES
print('Los AUTOVECTORES son:') for j in range(len(valores)):
print('AUTOVALOR: {} '.format(valores[j].round(2))) print('({};{};{})'.format(vectores[0][j].round(2),vectores[1][j].round(2),vectores[2][j].round(2))) print('Cada autovector representa las direcciones de Tensiones Principales segun le corresponda.') print('') #INVARIANTES
J1,lista=(Invariantes_escalar(N,M))
if J1==True:
print('-->El INVARIANTE ESCALAR en la matriz propuesta y la matriz de autovalores son IGUALES.') print('Invariantes Escalares:\n TENSOR DE INERCIA: {} \n MATRIZ DE AUTOVALORES: {}'.format(lista[0],lista[1])) else:
print('-->El INVARIANTE ESCALAR en la matriz propuesta y la matriz de autovalores son DIFERENTES.') print('Invariantes Escalares:\n TENSOR DE INERCIA: {} \n MATRIZ DE AUTOVALORES: {}'.format(lista[0],lista[1])) print('') J2,lista=Det_menor(N,M)
if J2==True:
print('--DETERMINANTE MENOR en la matriz propuesta y la matriz de autovalores son IGUALES.') print('Determinante menor:\n TENSOR DE INERCIA: {} \n MATRIZ DE AUTOVALORES: {}'.format(lista[0],lista[1])) else:
print('-->DETERMINANTE MENOR en la matriz propuesta y la matriz de autovalores son DIFERENTES.') print('Determinante menor:\n TENSOR DE INERCIA: {} \n MATRIZ DE AUTOVALORES: {}'.format(lista[0],lista[1])) print('') J3,lista=Det_mayor(N,M)
if J3==True:
print('-->DETERMINANTE MAYOR en la matriz propuesta y la matriz de autovalores son IGUALES.') print('Determinante Mayor:\n TENSOR DE INERCIA: {} \n MATRIZ DE AUTOVALORES: {}'.format(lista[0],lista[1])) else:
print('-->El DETERMINANTE MAYOR en la matriz propuesta y la matriz de autovalores son DIFERENTES.') print('Determinante Mayor:\n TENSOR DE INERCIA: {} \n MATRIZ DE AUTOVALORES: {}'.format(lista[0],lista[1])) print('') elif opcion=='s' or opcion=='S':
print('Saliendo...') break
else:
print('Opción no válida. Reintente.') '''
#AGREGADO
lista=list()
for i in range(3):
a=float(input('Valor para a{}:'.format(i))) lista.append(a)
R=np.array([lista])
print(R)
print(M*R)'''# PARA MULTIPLICAR UN VECTOR X CON LA MATRIZ CARGADA ANTERIORMENTE
3. Cálculo de Viga Isostática.
Este código fue hecho por el Sr. Mario Semañuk y busca realizar el rograma de Cálculo de Reacciones de vigas isostaticas simple
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Jan 13 16:10:29 2020
@author: Mario Semañuk
"""
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
print('\n',"--- Programa de Calculo de Reacciones de vigas isostaticas simples ---",'\n')
long=float(input("Ingrese la longitud de la barra en metros: "))
while long<=0: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
print("Error, Reingrese:")long=float(input())
print("\nIngrese el tipo de carga a utilizar:","\n1- Carga Puntual","\n2- Carga Uniformemente Distribuida")
tipo_carga=int(input())
while tipo_carga!=1 and tipo_carga!=2: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
tipo_carga=int(input("Error, reingrese: "))
if tipo_carga==1:
q1=float(input("Ingrese el valor de la carga en kN: "))while q1<=0: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
q1=float(input("Error, valor incorrecto, reingrese: ")) da=float(input("Ingrese la posición de la carga en la barra en metros: "))while da>long: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
da=float(input("Error, la carga debe estar sobre la barra, reingrese: "))rb=(q1*da/long)
ra=q1-rb
print("La reaccion del vinculo izquierdo es: ",str(ra)) print("La reaccion del vinculo derechoo es: ",str(rb))
if tipo_carga==2:
q1=float(input("Ingrese el valor de la carga en kN/m: "))while q1<=0: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
q1=float(input("Error, valor incorrecto, reingrese: ")) da=float(input("Ingrese la posición del inicio de la carga en la barra, en metros: "))while da>long: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
da=float(input("Error, la carga debe estar sobre la barra, reingrese:")) l=float(input("Ingrese la longitud de la carga: "))while l<=0 or l+da>long: #BUCLE DE REINGRESO
l=float(input("Error, la carga excede la barra, reingrese: "))rb=(q1*l)*(da+(l/2))/long
ra=(q1*l)-rb
print("La reacción del vínculo izquierdo es: ",str(ra)) print("La reacción del vínculo derechoo es: ",str(rb))""" Calculo de valores de corte y momento
Tomo 1000 puntos dentro de la barra
"""
valoresx=[] #LISTA DONDE SE GUARDARAN LAS ABSCISAS DE LOS GRAFICOS, ES DECIR, LAS N PARTICIONES DE LA LONGITUD DE LA BARRA
cortes=[] #LISTA DONDE SE GUARDARAN LOS VALORES DE CORTE DE LA BARRA
momentos=[] #LISTA DONDE SE GUARDARAN LOS VALORES DE MOMENTOS DE LA BARRA
ejey=[] #LA FORMA MAS RAPIDA QUE ENCONTRE DE GRAFICAR UN CERO PARA EL GRAFICO (LINEA HORIZONAL DE REFERENCIA)
etiquetasx=[] #LISTA DONDE SE GUARDARAN LAS 10 PARTES DE LA LONGITUD DE LA BARRA, SE UTILIZA PARA LAS ETIQUETAS DE LOS GRAFICOS
n=int(1000)
if tipo_carga==1:
for i in range(n):
valoresx.append(long*(i)/n) #VALORES DE DISTANCIA RELATIVOS AL ORIGEN DE LA BARRA, SE UTILIZAN PARA LOS CALCULOS DE CORTE Y MOMENTO
ejey.append(0) #AÑADE CEROS A LA LISTA PARA PODER GRAFICAR UNA LINEA HORIZONTAL
if i==0:
cortes.append(0) #AÑADE CERO COMO PRIMER VALOR
momentos.append(0) #AÑADE CERO COMO PRIMER VALOR
else:
if valoresx[i]<da: #CONDICION DONDE ESTOY ENTRE EL ORIGEN DE LA BARRA Y LA CARGA
cortes.append(ra)
momentos.append(-ra*valoresx[i])
if valoresx[i]>=da: #CONDICION DONDE ESTOY DESPUES DE LA CARGA
cortes.append(ra-q1)
momentos.append(-ra*valoresx[i]+q1*(valoresx[i]-da))
for i in range (11): #CREACION DE LAS ETIQUETAS PARA EL EJE X
etiquetasx.append(long*i/10)
cortes.append(0) #AÑADE CERO COMO ULTIMO VALOR
momentos.append(0) #AÑADE CERO COMO ULTIMO VALOR
valoresx.append(long) #AÑADE LA LONGITUD DE LA BARRA COMO ULTIMO VALOR
ejey.append(0) #AÑADE UN VALOR MAS A LA LINEA HORIZONTAL
fig, (ax1,ax2) =plt.subplots(2,1) #CREO DOS GRAFICOS, UNO POR ENCIMA DE OTRO (2 ROWS, 1 COLS)
ax1.plot(valoresx,cortes) #GRAFICA DE CORTE
ax1.plot(valoresx,ejey) #GRAFICA HORIZONTAL
ax1.set_xlabel ("Abscisas[m]") #TITULO DE EJE ax1.set_ylabel ("Cortes[kN]") #TITULO DE EJEax1.set_xticks(etiquetasx) #ETIQUETAS DEL EJE X
ax2.plot(valoresx,momentos) #GRAFICA DE MOMENTO
ax2.plot(valoresx,ejey) #GRAFICA HORIZONTAL
ax2.set_xlabel ("Abscisas[m]") #TITULO DE EJE ax2.set_ylabel ("Momentos[kNm]") #TITULO DE EJEax2.set_xticks(etiquetasx) #ETIQUETAS DEL EJE X
#DE ACA EN MAS, EL PROXIMO IF REALIZA LO MISMO QUE EL IF DE ARRIBA, PERO PARA CARGA DISTRIBUIDA
if tipo_carga==2:
for i in range(n):
valoresx.append(long*(i)/n)
ejey.append(0)
if i==0:
cortes.append(0)
momentos.append(0)
else:
if valoresx[i]<da: #DESDE EL ORIGEN DE LA BARRA HASTA DONDE COMIENZA LA CARGA
cortes.append(ra)
momentos.append(-ra*valoresx[i])
if valoresx[i]>=da and valoresx[i]<(da+l): #DESDE EL COMIENZO DE LA CARGA HASTA EL FINAL DE LA MISMA
cortes.append(ra-q1*valoresx[i])
momentos.append(-ra*valoresx[i]+q1*(valoresx[i]-da)*((valoresx[i]-da)/2))
if valoresx[i]>=(da+l): #DESDE EL FINAL DE LA CARGA HASTA EL FINAL DE LA BARRA
cortes.append(ra-q1*l)
momentos.append(-ra*valoresx[i]+q1*l*((valoresx[i]-da-(l/2))))
for i in range (11):
etiquetasx.append(long*i/10)
cortes.append(0)
momentos.append(0)
valoresx.append(long)
ejey.append(0)
fig, (ax1,ax2) =plt.subplots(2,1)
ax1.plot(valoresx,cortes)
ax1.plot(valoresx,ejey)
ax1.set_xlabel ("Abscisas[m]") ax1.set_ylabel ("Cortes[kN]")ax1.set_xticks(etiquetasx)
ax2.plot(valoresx,momentos)
ax2.plot(valoresx,ejey)
ax2.set_xlabel ("Abscisas[m]") ax2.set_ylabel ("Momentos[kNm]")ax2.set_xticks(etiquetasx)
4. Geometría de masas
Para introducir el conceto de Geometría de las Masa dejamos una Presentación ppt
También hay un video Explicativo sobre el uso del Código
Ver Presentación
Solución:
from cmath import pi
import math
def menu():
opcion = input("\nMenu:\na) Cargar Datos.\nb) Area del conjunto.\nc) Posicion del baricentro de la seccion.\nd) Momentos de segundo orden (Jx-Jy-Jxy).\ne) Momentos principales de inercia (Jmax-Jmin).\nS o s) Salir.\n...")
return (opcion.lower()) ##Para que retorne todo en minuscula
def A_Cj(dt): #dt = datos *A_Cj = Areas del conjunto
d_g = {}
Ar = (dt[1][0])*(dt[1][1])
At = (((dt[2][0])*(dt[2][1]))/2)
Ac = (-1*(dt[4][0])*(dt[4][1])) #-1 porque es un hueco
As = round(((math.pi)*((dt[3][0])**2)/2),3)
Atotal = (round((Ar + At + Ac + As),2))
d_g[1] = [Ar] #1 = Rectangulo
d_g[2] = [At] #2 = Triangulo
d_g[3] = [As] #3 = Semicirculo
d_g[4] = [Ac] #4 = Cuadrado7
d_g[5] = [Atotal] #5 = Area total
return d_g
def Pos_b_sec(d_calc,dt): #Posicion del baricentro de la seccion
##Rectangulo
Xgr = (round((dt[1][0]/2),3)*(d_calc[1][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
Ygr = (round(((dt[1][1]/2)+(dt[2][1])),3)*(d_calc[1][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
d_calc[1].append([Xgr,Ygr])
##Triangulo
Xgt = (round((dt[2][0]*(2/3)),3)*(d_calc[2][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
Ygt = (((dt[2][1]*(2/3)))*(d_calc[2][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
d_calc[2].append([Xgt,Ygt])
##Semicirculo
Xgs = (round((((4/3)*(dt[3][0]))/math.pi)+(dt[2][0]),3)*(d_calc[3][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
Ygs = (((dt[3][0]) + (dt[2][1]))*(d_calc[3][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
d_calc[3].append([Xgs,Ygs])
##Cuadrado
Xgc = (round((dt[1][0]/2),3)*(d_calc[4][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
Ygc = (((dt[2][1])+3.50)*(d_calc[4][0]))/(d_calc[5][0])
d_calc[4].append([Xgc,Ygc])
##Posicion del baricentro de la seccion
XG = Xgr+Xgt+Xgs+Xgc
YG = Ygr+Ygt+Ygs+Ygc
d_calc[5].append([XG,YG])
print("Posicion del baricentro de la seccion".center(100))
print("XG = {}".format(XG))
print("YG = {}".format(YG))
return True
def m_s_o_p(datos, result): #Momentos de segundo orden propios
form = [[1/12,1/36,1/128,-1/12],[1/12,1/36,1/145.77,-1/12],[0,-1/72,0,0]]
for i in range(3): #1v = Jx, 2v = Jy, 3v Jxy
for e in range(4):
if (i==0):
if (e==2):
jx = ((math.pi)*((2*(datos[e+1][0]))**4))*form[i][e]
result[e+1] = [jx]
else:
jx = (datos[e+1][0]*((datos[e+1][1])**3))*form[i][e]
result[e+1] = [jx]
elif (i==1):
if (e==2):
jy = ((2*(datos[e+1][0]))**4)*form[i][e]
result[e+1].append(jy)
else:
jy = (datos[e+1][1]*((datos[e+1][0])**3))*form[i][e]
result[e+1].append(jy)
else:
if (e==1):
jxy = (((datos[e+1][0])**2)*((datos[e+1][1])**2))*form[i][e]
result[e+1].append(jxy)
else:
result[e+1].append(0.0)
def dbp(calc,dt,result): #Distancia entre ejes baricentricos paralelos
XGr = (dt[1][0]/2)-((calc[5][1])[0])
YGr = (dt[1][1]/2)+(dt[2][1])-((calc[5][1])[1])
result[1].append(XGr)
result[1].append(YGr)
XGt = (dt[2][0]*(2/3))-((calc[5][1])[0])
YGt = (dt[2][1]*(2/3))-((calc[5][1])[1])
result[2].append(XGt)
result[2].append(YGt)
XGs = ((((4/3)*(dt[3][0]))/math.pi)+(dt[2][0]))-((calc[5][1])[0])
YGs = ((dt[3][0]) + (dt[2][1]))-((calc[5][1])[1])
result[3].append(XGs)
result[3].append(YGs)
XGc = (dt[1][0]/2)-((calc[5][1])[0])
YGc = ((dt[2][1])+3.50)-((calc[5][1])[1])
result[4].append(XGc)
result[4].append(YGc)
def m_s_o(calc, datos): #momentos de segundo orden
m_s_o_p_r = {} #momentos de segundo orden propios
d_b_p = {1:[],2:[],3:[],4:[]} #Distancia entre ejes baricentricos pararelos
m_s_o_b = {1:[],2:[],3:[],4:[],5:[]}
m_s_o_p(datos,m_s_o_p_r)
dbp(calc,datos,d_b_p)
Jxt = 0
Jyt = 0
Jxyt = 0
for i in range(4):
jx = (m_s_o_p_r[i+1][0])+((calc[i+1][0])*((d_b_p[i+1][1])**2))
Jxt+=jx
m_s_o_b[i+1].append(jx)
jy = (m_s_o_p_r[i+1][1])+((calc[i+1][0])*((d_b_p[i+1][0])**2))
Jyt+=jy
m_s_o_b[i+1].append(jy)
jxy = (m_s_o_p_r[i+1][2])+((calc[i+1][0])*(d_b_p[i+1][0])*(d_b_p[i+1][1]))
Jxyt+=jxy
m_s_o_b[i+1].append(jxy)
m_s_o_b[5].append(Jxt)
m_s_o_b[5].append(Jyt)
m_s_o_b[5].append(Jxyt)
return m_s_o_b
def Jm(m_b_p): #Momentos principales de inercia
Jxym = math.sqrt(((((m_b_p[5][0])-(m_b_p[5][1]))/2)**2)+((m_b_p[5][2])**2))
Jmax = (((m_b_p[5][0])+(m_b_p[5][1]))/2)+Jxym
Jmin = (((m_b_p[5][0])+(m_b_p[5][1]))/2)-Jxym
Alfa = (0.5*(math.atan(((2*m_b_p[5][2])/(m_b_p[5][1])-(m_b_p[5][0])))))
print("Momentos principales de inercia".center(100))
print("* Jxymax = {}".format(Jxym))
print("* Jmax = {}".format(Jmax))
print("* Jmin = {}".format(Jmin))
print("* α = {}".format(Alfa))
def main():
b1 = True
ba, bb, bc, bd= False, False, False, False
while (b1):
op = menu()
if op=='a':
print("\nIngrese los datos requeridos\n")
Datos={1: [],2:[],3:[],4:[],5:[]} ##Datos Geometricos
nombres=["Rectangulo","Triangulo","Semicirculo","Cuadrado","Total"] ##Datos Geometricos
for i in Datos:
b_d = True #Bandera de datos
while(b_d):
try:
if (i==1 or i==2 or i==4):
base = float(input("* Base del {}: ".format(nombres[i-1])))
if (base>0):
Datos[i].append(base)
altura = float(input("* Altura del {}: ".format(nombres[i-1])))
if (altura>0):
Datos[i].append(altura)
b_d = False
else:
print("\n¡ERROR! Reingrese...\n")
else:
print("\n¡ERROR! Reingrese...\n")
elif (i==3):
radio = float(input("* Radio del {}: ".format(nombres[i-1])))
if (radio>0):
Datos[i].append(radio)
b_d=False
else:
print("\n¡ERROR! Reingrese...\n")
else:
b_d = False
except ValueError:
print("\n¡ERROR! Reingresar...\n")
print("\n")
print("DATOS INGRESADOS EXITOSAMENTE".center(100))
for i in Datos:
print("* {}---->{}".format(nombres[i-1],Datos[i]))
ba = True
elif op=='b':
if (ba==True):
Calc_g = A_Cj(Datos)
print("AREAS".center(100))
for i in Calc_g:
print("* {} ----> {}".format(i,Calc_g[i]))
bb = True
else:
print("\n¡NO SE CARGARON LOS DATOS!\n")
elif op=='c':
if (ba==True and bb==True):
bc=Pos_b_sec(Calc_g,Datos)
else:
print("\n¡ACCESO DENEGADO!")
elif op=='d':
if (ba==True and bb==True and bc==True):
m_b = m_s_o(Calc_g,Datos) #Momentos baricentro
bd = True
print("Momentos de segundo orden".center(100))
for i in range(1,6):
print("\n{}".format(nombres[i-1]))
print("Jx = {}".format(m_b[i][0]))
print("Jy = {}".format(m_b[i][1]))
print("Jxy = {}".format(m_b[i][2]))
else:
print("\n¡ACCESO DENEGADO!")
elif op=='e':
if (ba==True and bb==True and bc==True and bd==True):
Jm(m_b)
else:
print("\n¡ACCESO DENEGADO!")
elif op=='s':
print("\n¡FINALIZANDO PROGRAMA!\n")
b1=False
else:
print("\n¡OPCION NO VALIDA!\n")
main()
5. Links de interés
- https://ingcivilocpvb.wordpress.com/tag/python/
- Longitud efectiva para el cálculo de pandeo de columnas de Hormigón Armado: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uUcrujR_lR0
- Determinación de diagrama de Momento Flector en barras https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tUUx1ho8Ypg
- Refuerzos de acero para vigas de Hormigón Armado (según EUROCODE 2) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FHT5VsXjFkA&t=28s
- Módulos de materiales https://github.com/buddyd16/Structural-Engineering
- Módulos de materiales https://bitbucket.org/struthonteam/strupy/wiki/browse/